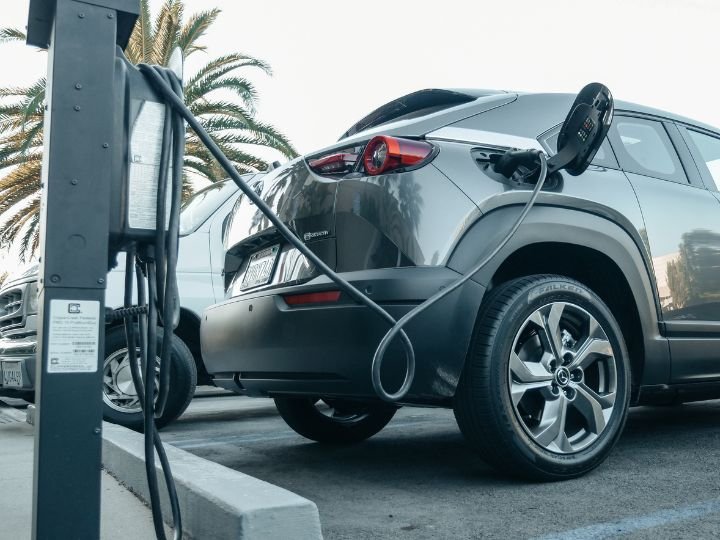
In recent years, the world has witnessed an accelerated shift toward sustainability, nowhere more evident than in the automotive industry. “Green tech auto” is not just a buzzword—it represents a sweeping transformation in how vehicles are designed, produced, and operated. As concerns over climate change, air pollution, and dwindling fossil fuels intensify, the demand for greener automotive solutions is reshaping the industry’s priorities. This article explores the evolution, innovations, benefits, challenges, and the road ahead for green tech auto.
The Evolution of Green Tech in Automobiles
The automotive industry has historically relied on internal combustion engines powered by gasoline or diesel. While these vehicles revolutionized mobility, they also became major contributors to carbon emissions and urban air quality issues. Early efforts at “green” innovation focused on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions with catalytic converters and unleaded fuel. However, these measures were only the beginning.
By the late 20th and early 21st centuries, mounting environmental pressures and advancing technology converged, igniting the green tech auto movement. The introduction of hybrid vehicles, like the Toyota Prius, marked a turning point. These vehicles combined traditional combustion engines with electric motors, offering improved fuel economy and reduced emissions.
Today, the evolution continues at a rapid pace, with electric vehicles (EVs), hydrogen fuel cell technology, and advanced materials propelling the green tech auto revolution.
Key Innovations in Green Tech Auto
Green tech auto encompasses a broad spectrum of innovations, all designed to reduce the environmental footprint of vehicles. Some of the most influential advancements include:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles are at the forefront of green tech auto. Unlike traditional cars, EVs are powered entirely by electricity stored in batteries. They produce zero tailpipe emissions and are often cheaper to operate due to lower fuel and maintenance costs. Companies like Tesla, Nissan, and Chevrolet have popularized EVs, while traditional automakers such as Ford and Volkswagen are investing heavily in electrification.
2. Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrids blend internal combustion engines with electric motors for improved efficiency. Plug-in hybrids go a step further, allowing drivers to charge the battery via an external power source and travel short distances on electricity alone. These vehicles serve as a transitional technology, easing consumers into fully electric mobility.
3. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. While still in the early stages of adoption, hydrogen-powered cars and trucks offer fast refueling and longer driving ranges, making them an attractive option for certain markets.
4. Regenerative Braking and Energy Recovery
Modern green tech autos often feature regenerative braking systems. When the vehicle slows down, the system captures kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat and stores it in the battery for later use. This innovation boosts overall efficiency.
5. Lightweight and Recycled Materials
Reducing vehicle weight improves fuel economy and reduces emissions. Automakers are increasingly using lightweight materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and high-strength steel. Additionally, recycled plastics and sustainable fabrics are making their way into car interiors.
6. Smart and Connected Technologies
Green tech auto isn’t just about the powertrain; it’s also about smarter operation. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), connected navigation, and apps that suggest eco-friendly routes all help minimize energy use and emissions.
7. Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
The green revolution extends to production lines as well. Automakers are investing in renewable energy, water recycling, and waste reduction at their facilities, making the entire vehicle lifecycle more sustainable.
The Benefits of Green Tech Auto
The adoption of green technology in the auto sector yields numerous benefits:
Environmental Impact
Green tech autos significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants. EVs, for instance, produce no tailpipe emissions, and even when accounting for electricity generation, they are often cleaner than their gasoline counterparts.
Cost Savings
Although green vehicles can have a higher upfront cost, they typically offer lower operating expenses. Electricity is cheaper than gasoline in many regions, and EVs have fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance costs.
Energy Independence
By shifting away from fossil fuels, green tech auto reduces dependence on imported oil, enhancing energy security for nations.
Economic Growth and Jobs
The green tech auto sector is a hotbed for innovation, driving job creation in fields such as battery manufacturing, software development, and renewable energy.
Improved Air Quality and Public Health
Lower emissions contribute to cleaner air, especially in urban areas, leading to health benefits and reduced healthcare costs.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite its promise, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of green tech auto:
Charging and Refueling Infrastructure
A robust network of charging stations and hydrogen refueling points is essential for mass EV and fuel cell adoption. Many regions, especially rural areas, still lack sufficient infrastructure.
Battery Technology and Recycling
While battery technology has advanced rapidly, concerns remain over range, charging time, resource extraction, and end-of-life recycling. Developing closed-loop recycling systems and alternative chemistries is a key industry focus.
Upfront Costs
Green tech autos, especially EVs and fuel cell vehicles, can be more expensive than conventional cars. However, falling battery prices and government incentives are helping to narrow the gap.
Consumer Awareness and Acceptance
Misinformation, range anxiety, and resistance to change persist among some consumers. Education and experiential marketing are crucial for overcoming skepticism.
Grid Capacity and Renewable Integration
As more vehicles plug into the grid, utilities must manage increased demand and integrate renewable energy sources to maximize environmental benefits.
The Role of Policy and Incentives
Government action is central to accelerating green tech auto adoption. Many countries offer tax credits, rebates, and other incentives to consumers and manufacturers. Stricter emissions regulations and bans on internal combustion engine sales, set for future dates in regions like the EU and California, are pushing automakers to prioritize green technologies.
Public investment in charging infrastructure, research and development grants, and support for renewable energy also play a significant role.
The Future of Green Tech Auto
Looking ahead, green tech auto will only become more integral to transportation. Automakers are racing to electrify their fleets, with some pledging to sell only electric or zero-emission vehicles within the next decade. Battery technology is set to improve further, with solid-state batteries promising greater range and faster charging.
Hydrogen fuel cells, autonomous driving, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration will continue to evolve. Shared mobility and smart city initiatives will further reduce the environmental footprint of transportation.
Ultimately, green tech auto is about more than just vehicles—it’s about reimagining mobility in a way that balances human progress with planetary stewardship.
Conclusion
Green tech auto is transforming the automotive landscape, offering practical solutions to urgent environmental challenges while delivering economic and social benefits. As technology advances and barriers fall, the vision of clean, efficient, and accessible transportation is within reach. Whether it’s through driving an electric car, supporting eco-friendly policies, or demanding greener choices, everyone has a role to play in driving the future of sustainable mobility.